Most people would be surprised to hear that the most advanced nuclear-tipped cruise missile ever put into operation was retired from service while its predecessor, a less survivable missile it was supposed to replace, soldiers on in U.S. Air Force service to this very day. This topsy-turvy reality is somewhat metaphorical of General Dynamics’ AGM-129 Advanced Cruise Missile (ACM) itself. In fact, the AGM-129 could be considered the second stealth aircraft to ever enter production, because that is what it really was, albeit one that was designed upside down, and for good reason.
The origins of the ACM are fairly straightforward. The AGM-86B Air-Launched Cruise Missile (ALCM) entered service in the early 1980s. When it was being designed, and while the non-production AGM-86A was undergoing initial trials, the best way to deliver a nuclear warhead deep inside Soviet airspace by an air-breathing platform was via low-altitude penetration. The AGM-86 was designed exactly for that, to punch through at treetop level using terrain contour matching, terrain-following radar, and inertial navigation to get close enough to a target that the W80 nuclear warhead onboard could do its job successfully.

Later on, the AGM-86C and D would integrate GPS to deliver pinpoint conventional strikes. You can read all about the AGM-86C/D’s capabilities in this recent piece of ours, but the nuclear-armed version of the era had no such accuracy. Regardless, survivability against quickly evolving Soviet air defenses was the most pressing requirement in the Air Force’s air-launched cruise missile portfolio as the 1970s gave way to the 1980s.

The AGM-86B had a few stealthy characteristics, but it was far from a true low observable design. Just as it came into service, the Air Force realized that the days when being able to beat air defenses via low-flying alone were coming to an end. Airborne early warning and control aircraft and advanced fire control radars with look-down-shoot-down capabilities, like those on Russia’s 4th generation fighter and interceptor fleets (Su-27 and MiG-31, specifically), would decrease the effectiveness of nap-of-the-earth flying tactics. Something far more survivable was needed, and fast.

Out of a handful of DARPA initiatives and studies dubbed TEAL DAWN that explored future cruise missile technologies and long-range bomber strategies, it was concluded that the new stealth bomber then in development alone wouldn’t be survivable against the densest Soviet air defenses. Long-range and survivable standoff weapons would be needed in part to mitigate those defenses. Two requirements were established—one stealthy missile that could travel around 1,500 miles or more and another that could travel over 5,000 miles. The latter clearly invalidated much of the need for a stealth bomber in the first place and it was thought that at least a decade would be needed to develop such a long-range weapon. As a result, it was jettisoned to concentrate on the shorter-ranged stealthy cruise missile requirement that could be fielded quickly and equip the Air Force’s new stealth bomber—at least that’s what they hoped. With this in mind, a competition to build such a weapon was quietly launched.
Lockheed, Boeing, and General Dynamics ended up squaring off in secret for this new contract. Lockheed’s Skunk Works leveraged their work on the F-117 program, which was just spinning up in a very secretive operational state at the time, to produce its F-117-shaped cruise missile, known under the code name SENIOR PROM. The details surrounding Boeing’s design remain unclear. General Dynamics’ design was a bit more of a traditional configuration, but one that was clean-sheet and packed with very stealthy features arranged in unique ways to maximize its effectiveness and efficiency. SENIOR PROM, which was a test program before competing for the Advanced Cruise Missile contract, was very stealthy, but it would have been troublesome fitting it into a bomber’s weapons bay. By 1983, General Dynamics clenched the contract and the AGM-129A Advanced Cruise Missile was officially born.

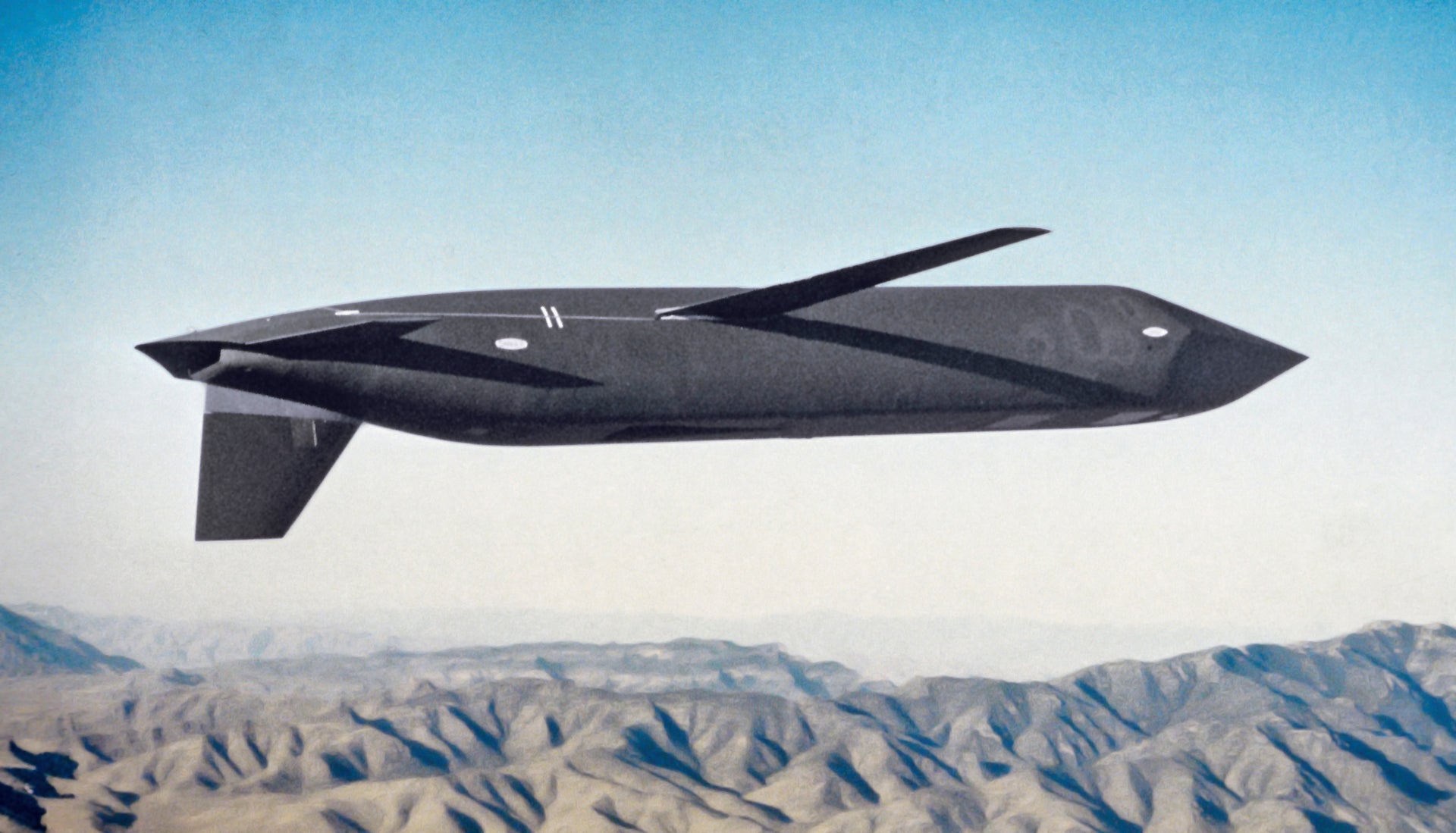
General Dynamics’ design, which measured nearly 21 feet long and weighed in at 3,700 pounds, was downright wicked looking. A faceted, stiletto-shaped fuselage with a chined, sharp-tip nose area and forward-swept pop-out wings gave it a sinister, almost Klingon-like look. Not just the wings were backward, all the low observable features were oriented towards defeating detection from above, not below. This resulted in an upside-down-looking airframe of sorts.
The vertical stabilizer-rudder pointed down instead of up. It was made up of composite materials, as were the missile’s horizontal forward-swept stabilizers, to remain nearly invisible to the most threatening radar bands. The vertical stabilizer was also offset to the left side of the fuselage’s centerline.

That gas from the missile’s two-dimensional exhaust aperture was blown over a platypus-like defuser structure that shielded its signature from, you guessed it, above, instead of below. The exhaust was also mixed with cold air to help further attenuate its infrared signature. Soviet infrared search and track (IRST) systems were advancing in capability at the time and included on all of Russia’s 4th generation fighter/interceptor designs, so infrared signature reduction was weighted heavily alongside radar cross-section reduction during the competition that led to the AGM-129.

The low-observable trapezoidal air inlet sat flush on the bottom of the missile instead of the top of it and fed the engine with air through a serpentine duct, thus eliminating any radar return from the engine fan face. Realizing a flush air inlet on something that flies at transonic speeds comes with major design challenges and it’s not like any stealthy air inlet configuration is easy to design or produce, to begin with. Beyond its underlying radar-evading structures, the AGM-129 was also covered with radar absorbent material and coatings and given an olive drab color to blend in with the terrain it would roar over just before sparking off a nuclear apocalypse.

So, if you think the AGM-129 looks like it is flying inverted, that is by very conscious design. Overall, the missile was designed with a particular weight put on stealth from its upper and forward aspects, where it was most vulnerable. From directly to its side, its radar signature was reduced, but more visible than from other angles. This was deemed a non-issue because the pulse-doppler radars that could threaten it from above are unable to detect low-flying targets hiding in ground clutter while flying at perpendicular angles to the radar antenna as they remain inside the radar’s “doppler notch.” You can read more about this phenomenon and the tactics associated with it here.
Navigation was also innovative. The AGM-129 introduced a laser doppler velocimeter into its navigational suite, which, like the AGM-86, also included inertial navigation and terrain contour matching. This gave it substantially better accuracy over long distances than the AGM-86B, which was designed less than a decade before it.
It also included laser detection and ranging system (LADAR) to aid in low-altitude flight, which further allowed it to fine-tune its endgame attack run down to as accurate as 90 feet according to stated metrics, although the system likely became even more accurate as it matured. Considering it still packed the same W80 variable yield warhead (5kt-150kt) as the AGM-86B, its better accuracy substantially increased its effectiveness, especially against reinforced targets or those that are partially shielded by terrain.
LADAR, as opposed to radar, also allowed the AGM-129 to remain electromagnetically silent, giving off no radio frequency energy when it was most vulnerable and thus making it even harder to detect. There were some tradeoffs though, LADAR could have trouble receiving data against certain surfaces, such as those that were extremely reflective or highly light absorbent. Still, the system was extremely effective and because the missile was so stealthy, it could fly at higher altitudes and in most cases still survive to make it to its target if need be.

Still, the system was not perfect. During one test over Dugway Proving Ground in 1997, an AGM-129 was flying so low it impacted some trailers belonging to an observatory. Nobody was hurt in the incident and the missile had been flying for three and a half hours before the accident. It turns out the mission planners had no idea the trailers were there and how the missile got so low was unclear to begin with.
The missile was fast, traveling at just under the speed of sound, and it also packed a very long range. It used a far more fuel-efficient engine, the Williams International F112-WR-100 turbofan, than the one found on the AGM-86, which gave it significantly greater range while retaining similar dimensions and the same payload. Officially, ACM could reach out 2,000 miles to its target , but it seems clear that its real range was actually significantly further, especially when flying a more efficient flight profile during more benign portions of its trip to its target area. As noted earlier, the missile’s high degree of stealth meant that it could climb to more efficient altitudes during certain phases of flight and still have a high chance of surviving to complete its horrific task.
Another interesting component of the AGM-129 was its computer system. From how it has been explained to me it used basically one central processor and computing system to run the vast majority of the missile’s functions. For early 1980s military technology, this is an amazing feat. Basically, the computer system and the system designed to used it on the missile was absolutely cutting-edge for its time.

It can’t be stressed enough how advanced the ACM was for its time. It had many elements that hadn’t yet emerged from the classified manned aircraft realm, but was an autonomous system meant to fly thousands of miles to its target without aid and to be built by the hundreds. It was truly a highly sensitive modern marvel of its era.
The first flight test of an AGM-129 occurred in July of 1985, with the first production missiles being delivered two years later, in 1987. It was that year when the program became public, as well. In that sense, it was the first disclosure of a stealth flying machine ever. Still, the program struggled early in its production run. There were technological issues that popped up in flight testing, but the major problems were with building the advanced missiles themselves. Remember, at the time of its first deliveries, no stealth aircraft had even been acknowledged by the Air Force. This wouldn’t occur until two years later when the F-117 was officially disclosed to the public. So, the technologies used in its manufacturing were absolutely cutting-edge in nature.
The missile’s very aggressive concurrent testing and production schedule concept and major labor issues with the International Association of Machinists began to cripple the program and it quickly became a pariah on Capitol Hill and in certain parts of the Pentagon. By the end of the decade, the AGM-129 was being declared a fiasco. Things got so bad with quality control issues that production was halted between 1989 and 1991.

Of course, the timing of this setback couldn’t have been worse. The Cold War was ending and the defense budget was set to snap back hard, especially in terms of strategic weaponry. In addition, the B-2 wouldn’t fly until 1989 and still would have a long developmental road ahead of it. The B-1B was also having its own troubles and the missile was never designed to fit in its weapons bays, it was too long, and eventually, the B-1B would lose its nuclear role altogether. So, the weapon that was procured at least in part to be paired with the stealth bomber would be relegated to the B-52.
The confluence of these factors, as well as the START treaty which limited these types of weapons, resulted in a drastic reduction of the programmed buy. The nearly 1,500 missiles needed to replace the AGM-86B in full was slashed down to less than half that, and eventually to a final number of just 460 missiles. Unit cost soared partially as a result of the curtailed order, with each missile costing roughly $4.3 million in 1992 dollars. This is extremely expensive for a cruise missile even by today’s standards. A decade earlier, the AGM-86Bs cost around $1.3 million each. The ACM had truly entered a Pentagon budgetary ‘death spiral’ alongside the plane that was supposed to carry it, the B-2.

Still, they were the most advanced cruise missiles in the world and the truncated force of 460 missiles soldiered on over the next two decades, exclusively equipping the B-52 force. A single B-52 could carry 20 of the missiles at one time. Six on each wing pylon and eight in the jet’s cavernous weapons bay on a rotary launcher.
Two other AGM-129 variants were proposed, but never came to fruition. The AGM-129B was a shadowy initiative to equip a revised design with an axial-flow jet engine, new software, and a different nuclear warhead to take on a specialized role that remains classified. This could have been a GPS-equipped, imaging infrared, or otherwise more precise upgrade of the weapon that would also be equipped with a penetrating nuclear warhead of a lower yield to take on heavily fortified bunkers and more hardened structures. Then again, maybe it was something more exotic, we just don’t know for absolute certain.

The other proposed variant was a conventional land attack model similar to the AGM-86C/D Conventional Air-Launched Cruise Missiles (CALCM), but far more survivable and with a lot longer reach. GPS would have been necessary for this weapon, just like it was for its CALCM progenitor. An imaging infrared seeker with imaging matching could have been injected into the design for even better accuracy. In retrospect, this would have been a relatively amazing weapon.
The ACMs that were built may have received a GPS upgrade sometime during the decade and a half or so that followed their introduction into service in 1990, although it remains unclear if this actually happened. It would have given the missiles pinpoint accuracy, but GPS connectivity would not be assured during a nuclear war and it may have been cost-prohibitive to integrate a GPS antenna onto the ACM’s stealth airframe. If the upgrade did happen, it would have likely occurred when the missiles were put through a Service Life Extension Program (SLEP) in the early 2000s that would allow them to serve until 2030 and possibly beyond.

Regardless of this life extension program, in 2007, the 17th year of the AGM-129’s operational service, it was decided that the entire ACM force would be drawn down and eliminated from service by the end of 2012. A number of factors contributed to this decision, the first being the post 9/11 focus on counter-insurgency operations instead of preparing for peer state conflicts. The U.S. had two raging wars on its hands that were anything but cheap, and the Russian bear remained largely dormant at the time, while China was just on precipice its economic, geopolitical, and technological rise. The AGM-129 program, with its relatively small fleet made up of super high-tech 1980s technology, meant that sustaining the missiles was far from a cheap or easy task. The AGM-86B, although much less survivable, checked a box for much less money and had commonality with its conventionally armed cousin, the AGM-86C/D, which helped significantly in terms of sustainment scalability.
Beyond fiscal matters, the Strategic Offensive Reductions Treaty (SORT) with Russia also meant more warheads would be pulled off the front lines. So, the Air Force moved forward with not just retiring the AGM-129, but destroying the fleet, a task that was completed as planned by the end of 2012.
During its drawdown period, one highly publicized and unfortunate event occurred with what were historically very shy missiles. On August 30th, 2007 a “Bent Spear” incident occurred with a package of 12 ACMs. A B-52H was set to ferry unarmed ACMs from Minot AFB in North Dakota to Barksdale AFB in Louisiana. The missiles were to be decommissioned at Barksdale, so the mission itself wasn’t necessarily out of the ordinary. What was not normal is that six of the missiles were actually carrying their W-80 thermonuclear warheads.
The nuclear-armed B-52 sat overnight without a proper security detail and other precautions until the crew showed up for the mission the next day. During pre-flight checks, the crew did not inspect both pylons loaded with missiles. They only inspected the one that held six unarmed ACMs, but logged that both pylons full of missiles were indeed checked and that they were unarmed. The crews then flew across the Midwest not knowing they were carrying six nuclear warheads.

After arriving at Barksdale, the jet sat for another eight hours without standard precautions associated with nuclear-armed aircraft. It was nearly a day and a half after the Minot AFB personnel blew off normal procedures and loaded the hot ACMs on the B-52 that the fact that the plane was actually carrying live warheads was discovered. The incident was the first of its kind in four decades and sent shockwaves through the Air Force and the Pentagon. A subsequent investigation showed horrible disregard for critical nuclear weapons handling protocols and everyone from four unit commanders down to those directly involved were heavily disciplined or removed from duty. All nuclear weapons handling was suspended at Minot AFB. It also resulted in a new set of procedures that were designed to make sure such a breakdown in procedures doesn’t happen again.
It was a sad end to the troubled development and career of the world’s first stealth cruise missile.

In retrospect, the decision not just to retire, but fully destroy the AGM-129 cadre seems like a very poor one. Today, the Air Force is working on developing a new stealthy long-range nuclear-tipped cruise missile, the Long-Range Stand-Off (LRSO) weapon, a program that will cost tens of billions of dollars and won’t produce an operational missile until at least 2030. Raytheon, which owns the AGM-129 design after it bought Hughes Missile Systems, which bought General Dynamics’ missile portfolio prior, is competing with Lockheed for the LRSO contract. In the meantime, the AGM-86B is supposed to remain a viable deterrent even in an era of ever more capable highly integrated air defense systems, ones that now rely on look-down-shoot-down sensors more than they did 35 years ago and that are far more advanced in general than what existed when ACM was conceived. This begs the question, is the AGM-86B really a survivable deterrent at all? The true answer, that we will never officially get, is probably less comforting than we may want to hear.
The truth is, the AGM-129 was way ahead of its time. Today, there are numerous stealthy cruise missiles in production or will be in production soon and they are becoming an extremely sought-after item. The USAF can’t get enough of Lockheed’s JASSM family of missiles, which continues to rapidly grow in capability, while the Navy is procuring the anti-ship LRASM cousin of JASSM, the stealthy Naval Strike Missile, and a powered version of the JSOW. Multiple foreign militaries have their own stealthy cruise missiles, as well. But these are conventionally armed weapons. It will be at least another decade until a nuclear-armed stealth cruise missile hits the USAF’s inventory again. That weapon, the LRSO, will be in many ways the son of AGM-129 and from what we are hearing, it will be absolutely loaded with the latest and greatest technology that will allow it to survive in the most inhospitable of combat environments. It is also meant to equip the USAF’s new stealth bomber, the B-21 Raider.
Somehow this all sounds eerily familiar, doesn’t it?
Contact the author: Tyler@thedrive.com